As defined by most of the scholastic articles, the traditional security architecture is built on ‘castle-and-moat’ concept, but things are gradually changing – a new concept called Zero Trust is catching up. As per the traditional concept, once the person or device is authenticated, he or the device can access the resources within the perimeter of the network but as per the new concept (Zero Trust), even the person or the device is authenticated, they cannot move freely or access data at their will. They will be entrusted with a restricted access.
Although the concept has been floating in the market for last 10 years, ever since Forester coined it but people were not convinced about it therefore not taking it so seriously. But as the situation of Covid 19 Pandemic is panning out and attacks like malware, impersonation of identity, email extortion campaigns, worms, phishing attacks, botnet, etc. have happened in these 45 days. Large very secured companies like Cognizant and LinkedIn have borne the brunt of the attackers, every CISO is now taking it seriously. Therefore, Zero Trust Security appearing to be the future of the information security.
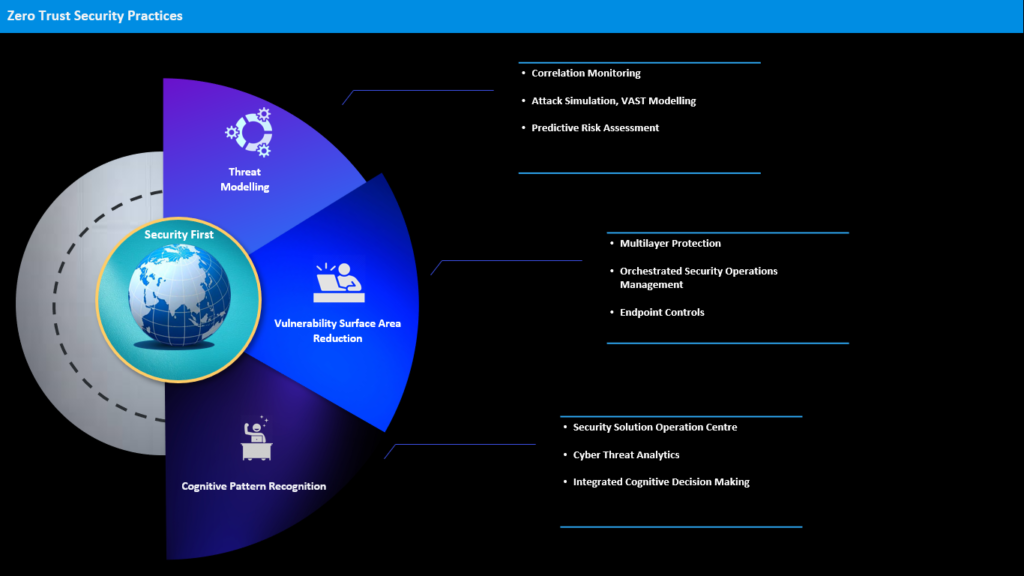
Zero Trust Security prescribes many procedures to isolate intruders. One of those is surface area reduction by microsegmentation. Microsegmentation is not new in network but in DC and compute it makes logical units with own unique security policies. By doing so, it limits the malicious actors to a restricted surface and easily traces if there is unwanted east-west or north-south traffic.
Secondly, Zero Trust Security advocates for a threat modeling of no one is trusted by default from inside or outside the network, and verification is required from everyone trying to gain access to resources on the network. It means Multi-factor authentication (MFA) is also a tenet of this new concept which askes your password along wide 2FA to authenticate yourself. It also prescribes least-privilege access, which offers the users very limited access as per the company policy parameter – not beyond that. This obviously reduces the chance of exposing sensitive data.

As far as devices are concerned, Zero Trust also monitors and controls different devices accessing network – again a step further to reduce the coverage area.
Of course, Zero Trust Security also advocates for cognitive pattern recognition of the attacks by integrating machine learning with forensic network analytics. It automates identification of the modus operandi of the actors and therefore nullifies the attempts.

So, in a nutshell, Zero Trust Security induces to review existing asset management policies, reduces and restricts overly permissive rules, strengthens vulnerable points and makes attack surface smaller. It also means taking control of IT security completely.
Greg Bryan, Senior Manager, Enterprise Research at TeleGeography, says, “Zero Trust Security is making the move from buzzword to serious consideration.”
But the question is since it is not a technology, can it be right practice or there is technology which creates a canopy of Zero Trust in the network? The other question is: what about customers, who want free access to their resources outsourced to the service providers? Would they be happy about sailing in a restricted zone in their own resources?
“The challenge for CIOs is to understand the foundations necessary to make ZTS a viable security solution. For example, in order to have user or device-based security policies, you first need to identify every user and device on your network—no small task for many enterprises. Regardless, any time a new architecture is proposed there will be hesitation and a period of assessment before adoption ramps up,” he added.
“Interest in Zero Trust Security remains high among WAN managers, while only 8% have implemented the IT security model. 31% are considering Zero Trust Security, 19% are in the adoption phase with a fifth of respondents unfamiliar with the concept.”
Mind it, as per a report new organization falls victim to ransomware every 14 seconds. The period will further contract to 11 seconds by 2021 and damages would reach beyond $11.5 billion.


