Insider threats, driven by personal motivations and enabled by the rapid evolution of technology and changing hybrid work environments, present a critical challenge to organizational security. Addressing these threats necessitates a sophisticated, multifaceted approach that combines advanced detection technologies, continuous monitoring, and a strong emphasis on employee training and awareness.
Securonix recently surveyed 467 cybersecurity professionals across diverse sectors, seeking to uncover the nature of insider threat challenges faced by organizations, focusing on understanding the factors driving these threats, their detection and mitigation complexities, and the effectiveness of insider threat programs.
Key survey findings include:
- Rise in Insider Attacks: From 2019 to 2024, the number of organizations reporting insider attacks increased from 66% of organizations to 76%, indicating a substantial increase in detected insider threats. Notably, there’s a rise in incidents with multiple attacks per year, underscoring the urgent need for enhanced detection and mitigation strategies, including continuous monitoring and proactive defenses.
- High-Risk Insiders and Motivations: There has been a marked increase in concern for malicious insiders, rising from 60% in 2019 to 74% in 2024, indicating a heightened awareness or experience of intentional insider attacks. Financial gain leads the list of motivations organizations are most concerned about.
- Detecting Insider vs. External Attacks: 90% of respondents report insider attacks as equally or more challenging to detect than external attacks, highlighting the complexity of insider threats. Only 16% of organizations consider themselves extremely effective in handling insider threats, an improvement from 11% in 2019, yet there is still significant room for enhancing threat management strategies.
- Ransomware Threat: 76% of organizations report an increasing prevalence of ransomware and triple extortion techniques in their environments, highlighting a growing cybersecurity concern. Information disclosure (56%) and unauthorized data operations (48%) are also leading concerns, emphasizing the importance of data-centric security measures and robust identity and access management controls.
- Hybrid Work and Evolving Tech: 70% of respondents express concern about insider risks in hybrid work contexts, reflecting the challenges of securing distributed, less controlled environments. A majority of 75% are concerned about the impact of emerging technologies like AI, the Metaverse, and Quantum Computing on insider threats, indicating worries about their misuse and the potential to amplify threat capabilities.
- Insider Threat Program Maturity: While 66% of organizations feel vulnerable to insider attacks, 41% of organizations have only partially implemented insider threat programs, pointing to a lack of comprehensive activity monitoring and advanced threat management. Only 29% of respondents feel fully equipped with the right tools to protect against insider threats, indicating a significant gap in many organizations’ security capabilities.
Insider vs External Attacks
The perception of the difficulty in detecting and preventing insider attacks, as compared to external cyberattacks, has shifted noticeably in the last 5 years.
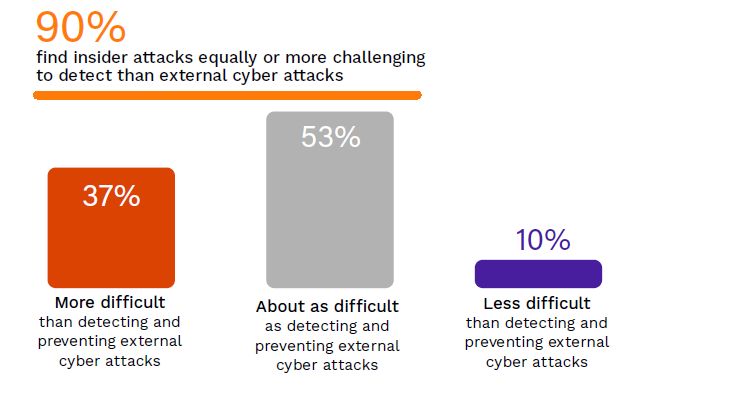
In 2024, an overwhelming majority of 90% of respondents report that insider attacks are as difficult (53%) or more difficult (37%) to detect and prevent compared to external attacks, up from a combined 50% who held this view in 2019. This significant increase suggests a growing awareness of the subtlety and complexity of insider threats compared to external ones.
How difficult is it to detect and prevent insider attacks compared to external cyberattacks?
Shifting Insider Threat Concerns
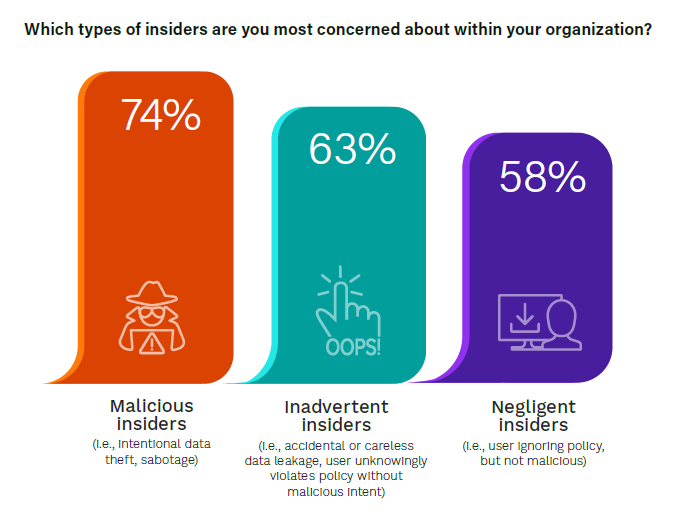
The survey data indicates a shift in the perception of insider threats over the last 5 years. There has been a marked increase in concern for malicious insiders, rising from 60% in 2019 to 74% in 2024, indicating a heightened awareness or experience of intentional insider attacks. However, concerns about inadvertent
insider incidents have slightly decreased from 71% in 2019 to 63% in 2024, perhaps indicating improved training, awareness, policy, and technological safeguards within some organizations or across some sectors.
Organizations should continue to enhance their strategies against malicious insiders by investing in advanced behavioral analytics and insider threat detection systems. It’s also crucial to emphasize employee training and maintain a culture of security awareness to prevent inadvertent and negligent incidents.
Changing Insider Motives
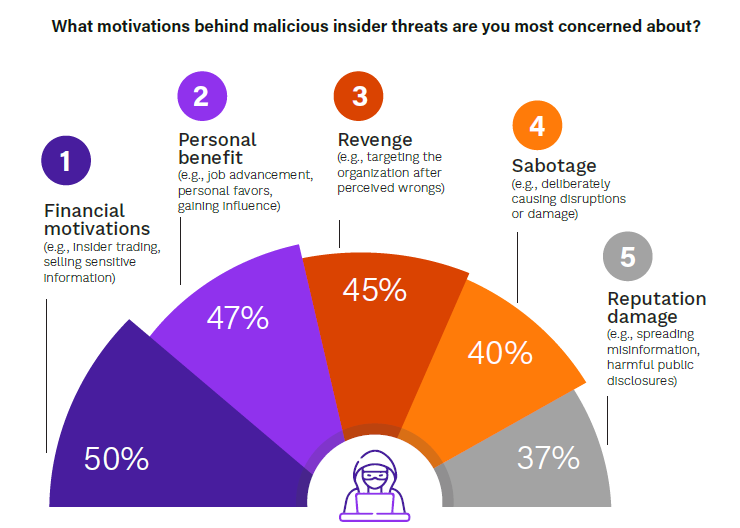
The most notable change in the past 5 years is the dramatic increase in concerns regarding personal benefit as an insider motive, which has risen from rank #6 in 2019 (15%) to #2 in 2024 (47%). Traditional fears such as financial motivations (50%) and revenge (45%) remain high, while sabotage decreased slightly (from 43% to 40% respectively). Notably, a significant increase in insider threats for reputational damage (from 8% to 37%) reflects the growing importance of public perception.
Organizations should consider implementing insider threat programs that include psychological elements and incentives alignment to counteract the risk of employees being swayed by personal gain or external influences. It’s also crucial to foster a culture where ethical conduct and reporting of suspicious activities are encouraged and rewarded.
Critical Data at Risk
Financial data is perceived as the most vulnerable, with 44% of respondents highlighting it, likely due to its direct monetization potential. Customer data, at 41%, follows closely, pointing to concerns over the loss of personally identifiable information (PII). Employee data is also a significant concern at 37%, signaling an awareness of the risks posed by the mishandling of sensitive personnel information. It is notable that a considerable 31% believe all company-sensitive data is susceptible, reflecting a broader concern for organizational data security.
Proactive measures such as data access controls, encryption, and employee training can mitigate the risk of insider attacks and threats to data confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Emphasizing the protection of the most vulnerable financial, customer, and employee data as part of a comprehensive data security strategy is imperative.



